Learn how statins, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and blood thinners work.
Understanding Heart Disease Medications: A Comprehensive Guide to Statins, ACE Inhibitors, and More
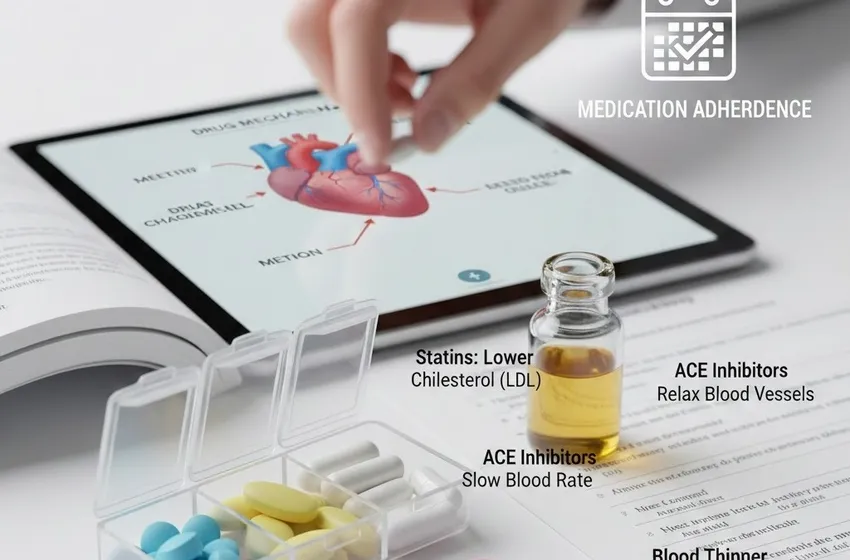
Managing cardiovascular health often feels like learning a new language. When a doctor hands you a prescription, you aren’t just receiving a pill; you are receiving a specific tool designed to alter your biology in a way that saves your life. To truly take charge of your health, you must understand the drug mechanisms behind these treatments—how they talk to your cells, relax your veins, and protect your heart muscle.
This guide simplifies the most common classes of heart medications, from the cholesterol-fighting power of statins to the pressure-relieving effects of ACE inhibitors.
Statins: The Cholesterol Commanders
Statins are perhaps the most recognizable name in heart health. Their primary mission is simple: lower "bad" cholesterol (LDL) to prevent plaque from clogging your arteries.
How They Work
The drug mechanisms of statins involve a specific enzyme in the liver called HMG-CoA reductase. This enzyme is the primary engine your body uses to produce cholesterol. Statins "clog" this engine, forcing the liver to stop producing its own cholesterol and instead pull existing LDL cholesterol out of your bloodstream to use for bodily functions.
Statin Side Effects
While highly effective, patients often express concerns about statin side effects. The most frequently reported issue is muscle pain or soreness, known as myalgia. In very rare cases, this can progress to rhabdomyolysis, a serious condition where muscle tissue breaks down. Other potential side effects include increased blood sugar levels, digestive upset, and liver enzyme fluctuations.
ACE Inhibitors: Relaxing the Pressure
ACE inhibitors (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors) are the frontline defense against high blood pressure and heart failure.
How They Work
The body uses a chemical called Angiotensin II to tighten blood vessels and increase blood pressure. ACE inhibitors work by blocking the enzyme that creates this chemical. By preventing the production of Angiotensin II, your blood vessels remain relaxed and open (dilated). This lowers your blood pressure and makes it much easier for your heart to pump blood to the rest of your body.
Commonly prescribed ACE inhibitors include Lisinopril, Enalapril, and Ramipril. The most notable side effect is a persistent, dry cough.
Beta-Blockers: Slowing the Pace
If your heart is a car engine that is "redlining" or working too hard, beta-blockers act as the speed governor.
How They Work
Beta-blockers function by blocking the effects of adrenaline (epinephrine) on your heart's beta receptors. By muting the "fight or flight" response, these drugs cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force. This reduces the heart's oxygen demand and lowers blood pressure.
They are essential for patients who have suffered a heart attack or those managing arrhythmias and chest pain. By slowing the heart, they allow it more time to fill with blood between beats, increasing overall efficiency.
Blood Thinners: Preventing the Blockage
Despite the name, blood thinners don't actually make your blood more watery. Instead, they make it less likely to form dangerous clots.
How They Work
There are two main categories of blood thinners: Anticoagulants (like Warfarin or Apixaban), which interfere with chemical clotting factors, and Antiplatelets (like Aspirin or Clopidogrel), which keep platelets from sticking together. The primary risk is increased bleeding, but preventing a stroke or heart attack is usually worth the risk of minor bruising.
The Critical Role of Medication Adherence
No heart medication can work if it stays in the bottle. Medication adherence—taking your pills exactly as prescribed—is the single most important factor in long-term survival for heart patients. Because heart disease is often a "silent" condition, you may not feel your blood pressure dropping, but stopping medications abruptly can cause a dangerous "rebound effect."
Tips for Success:
- Use a Pill Organizer to prevent missed doses.
- Set Phone Alarms for consistency.
- Communicate Side Effects like statin side effects to your doctor immediately instead of stopping the drug.
Summary Table
| Medication Class | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Statins | Lower LDL cholesterol | Prevents plaque buildup |
| ACE Inhibitors | Dilate blood vessels | Lowers blood pressure |
| Beta-Blockers | Slow heart rate | Reduces heart workload |
| Blood Thinners | Prevent clot formation | Reduces risk of stroke |
Conclusion
Understanding the drug mechanisms of your prescriptions empowers you to have better conversations with your healthcare provider. Whether managing beta-blockers or statin side effects, being informed makes you a participant in your own healing.
``` Would you like me to generate a list of specific questions you can ask your cardiologist about these medications during your next visit?