Discover why magnesium is the "chill pill" of the internet.
Magnesium: The "Chill Pill" of the Internet
In the high-stress landscape of 2025, a quiet mineral has become the undisputed "it-girl" of the wellness world. If you’ve spent any time on social media recently, you’ve likely seen the viral "Sleepy Girl Mocktail" or influencers touting the life-changing benefits of their evening supplements. Magnesium—once a humble mineral found in spinach and nuts—is now being hailed as the "chill pill" of the internet.
But why now? And more importantly, why are there so many different types? The sudden explosion in magnesium’s popularity isn’t just a trend; it’s a response to a collective crisis of burnout, insomnia, and cognitive fatigue. To truly unlock the benefits of this "miracle mineral," one must navigate the complex world of chelation, bioavailability, and targeted delivery.
Why Magnesium Went Viral: The Stress-Deficiency Loop
The internet’s obsession with magnesium is rooted in a very real biological problem. Modern agricultural practices have depleted our soil of essential minerals, and the standard processed diet often lacks the magnesium-rich leafy greens and seeds our ancestors consumed.
Furthermore, we live in a state of "stress-induced magnesium loss." When the body is under stress, it excretes magnesium through the urine. This creates a "vicious cycle": stress lowers your magnesium levels, and low magnesium levels make you more reactive to stress. By the time 2024-2025 rolled around, a global population feeling the effects of chronic cortisol elevation found their answer in the "chill pill."
Differentiating the Forms: Glycinate vs. L-Threonate
The most critical part of the magnesium conversation is the "carrier" molecule. Magnesium is rarely sold alone; it is typically bound to another substance to stabilize it. This binding determines where the mineral goes in your body.
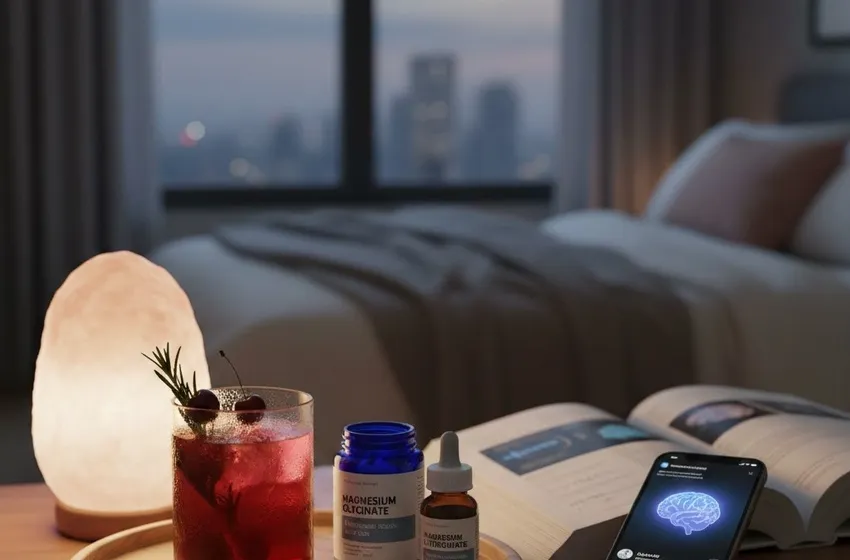
1. Magnesium Glycinate: The Anxiety and Sleep Specialist
If you are looking for an anxiety supplement that actually delivers on its promises, magnesium glycinate is the gold standard. In this form, magnesium is bound to glycine, an amino acid known for its own calming effects on the brain.
-
Primary Benefit: It acts as a potent sleep aid by increasing GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) levels, which helps "turn off" the racing thoughts that keep you awake at night.
-
The Difference: Unlike magnesium citrate (the kind in "natural calm" powders that can cause a laxative effect), glycinate is highly stable and has a superior absorption rate. It is gentle on the stomach and focuses its energy on relaxing the central nervous system and muscles.
2. Magnesium L-Threonate: The Brain Fog Buster
While glycinate works on the body and general anxiety, magnesium L-threonate is the only form specifically designed to penetrate the "blood-brain barrier." This is a selective filter that keeps most substances out of the brain—including most other forms of magnesium.
-
Primary Benefit: It is the ultimate tool for clearing brain fog and enhancing cognitive "bandwidth."
-
The Science: By increasing the density of synapses (the connections between neurons), L-Threonate supports neuroplasticity. Users often report sharper focus, better memory recall, and a "brighter" mental state during the day.
-
Best Use: Use this form in the morning or early afternoon to combat midday fatigue and mental exhaustion.
The Critical Importance of the Absorption Rate
When people say "magnesium didn't work for me," they are usually talking about magnesium oxide. This is the cheapest form found in most grocery store multivitamins. Unfortunately, magnesium oxide has an absorption rate as low as 4%. This means 96% of what you swallow is simply passing through your digestive tract—often causing diarrhea—without ever entering your cells.
To achieve true stress relief, you must choose chelated forms (like glycinate or L-threonate). These are recognized by the body as organic compounds rather than inorganic salts, allowing them to be absorbed much more efficiently into the bloodstream.
Summary: Crafting Your Magnesium Protocol
The internet’s love for magnesium is well-earned. In a world that is increasingly "wired and tired," this mineral provides a biological "reset button."
-
For the "Wired" (Anxiety/Insomnia): Stick to magnesium glycinate 30 minutes before bed.
-
For the "Tired" (Brain Fog/Poor Memory): Incorporate magnesium L-threonate into your morning routine.
-
For General Health: Look for a "complex" that includes both to ensure a high absorption rate and comprehensive stress relief.
By moving beyond the hype and understanding the chemistry, you can turn a viral trend into a foundational pillar of your mental health.