Explore NMN and NR as NAD precursors
NAD Boosters: The Anti-Aging Hype vs. Science
In the quest for the fountain of youth, few molecules have captured the public imagination—and the scientific spotlight—quite like NAD . Once a humble coenzyme known only to biochemists for its role in metabolism, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD ) is now the centerpiece of a multi-billion dollar longevity industry.
The surge in popularity is driven by a simple, sobering biological fact: as we age, our NAD levels plummet. By the time we reach middle age, our levels are roughly half of what they were in our youth. This decline is linked to nearly every hallmark of aging, from sluggish metabolism to DNA instability. Consequently, longevity supplements designed to replenish these levels have moved from niche biohacking forums to the mainstream.
At the heart of this NAD revolution are two primary NAD precursors: NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) and NR (Nicotinamide Riboside). This article explores the viral status, biological mechanisms, and the rigorous anti-aging science behind these potent molecules.
What is NAD and Why Does It Matter?
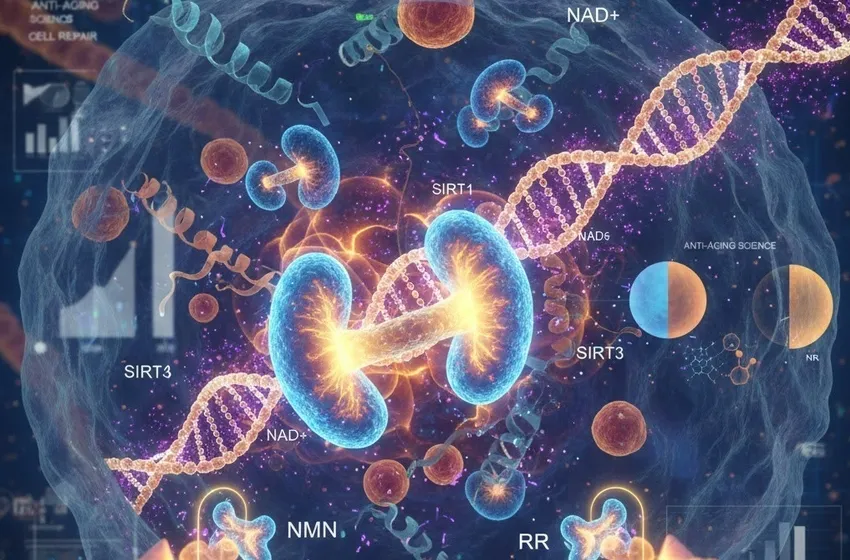
To understand why people are obsessed with NMN and NR, we first need to understand the role of NAD in the human body. NAD is a coenzyme found in every living cell, and it is essential for two primary functions:
- Cellular Energy Production: NAD acts as a shuttle, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. It is the critical spark plug in the mitochondria—the powerhouses of our cells—that allows them to convert nutrients from food into cellular energy (ATP).
- Cellular Repair and Defense: Beyond energy, NAD is a required fuel for enzymes that protect the cell. The most notable among these are sirtuins, a family of proteins often called the guardians of the genome.
The Mitochondrial Connection
Mitochondrial function is the bedrock of vitality. When NAD levels are high, mitochondria efficiently produce energy and clear out metabolic waste. When NAD levels drop, mitochondria become dysfunctional, leading to a state of cellular exhaustion that manifests as fatigue, cognitive decline, and metabolic disorders.
The Contenders: NMN vs. NR
While you cannot simply swallow a pill of NAD (it is too large a molecule to be efficiently absorbed by cells), you can take its building blocks. These are the NAD precursors.
1. NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
NMN has achieved viral status largely due to the work of Harvard geneticist Dr. David Sinclair. It is a direct precursor to NAD . In the metabolic pathway, NMN is just one enzymatic step away from becoming the final NAD molecule.
Mechanism: For years, it was debated whether NMN could enter cells directly. However, the discovery of the Slc12a8 transporter—a specific doorway for NMN in the gut and other tissues—suggests that NMN can be absorbed rapidly and converted into NAD to boost cellular energy systemicly.
The Viral Status: NMNs popularity exploded on social media and podcasts, fueled by claims of reversed biological age in mice and improved muscle insulin sensitivity in human trials.
2. NR (Nicotinamide Riboside)
NR is often considered the older brother of NMN in the supplement world. It was the first precursor to gain widespread commercial availability and has been extensively studied in human clinical trials.
Mechanism: NR enters the cell through a different set of transporters. Once inside, it is converted into NMN, which is then converted into NAD .
Benefits: Research into NR has highlighted its potential for reducing systemic inflammation and supporting brain health, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative concerns.
Sirtuins: The Longevity Switch
One of the most exciting aspects of anti-aging science is the relationship between NAD and sirtuins.
Sirtuins are enzymes that regulate cellular health. They are responsible for:
- DNA Repair: Fixing the daily breaks in our genetic code.
- Gene Expression: Turning off bad genes that promote aging and inflammation.
- Circadian Rhythms: Regulating our internal clock for better sleep and recovery.
However, sirtuins are NAD -dependent. Think of sirtuins as the CEO of the cell and NAD as the salary. If the salary isn't paid, the CEO stops working. By using longevity supplements like NMN or NR, we are essentially ensuring that our sirtuins have the budget they need to keep the cellular machinery running smoothly.
The Scientific Reality: What Does the Research Say?
While the hype is massive, the anti-aging science is still evolving.
Human Clinical Trials
In 2023 and 2024, several landmark human trials provided clarity. One study in middle-aged sedentary adults showed that NMN supplementation significantly increased walking distance and aerobic capacity. Another study involving NR showed improvements in the NAD levels of the brain, suggesting potential neuroprotective benefits.
The Metabolic Impact
Improving mitochondrial function isn't just about living longer; it is about living better. Research suggests that boosting NAD can:
- Enhance insulin sensitivity (combatting Type 2 Diabetes).
- Reduce arterial stiffness (improving heart health).
- Boost physical endurance and recovery.
2025 Regulatory Update: NMNs Legal Comeback
It is important to note the legal landscape of longevity supplements. In late 2022, the US FDA initially ruled that NMN could not be marketed as a dietary supplement because it was being investigated as a new drug.
However, as of late 2025, a series of regulatory reversals and successful New Dietary Ingredient (NDI) notifications have reinstated NMNs status in many jurisdictions. This has once again opened the gates for consumers to access high-quality NMN alongside NR.
How to Choose an NAD Booster
| Feature | NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) | NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) |
|---|---|---|
| Pathway | Direct precursor to NAD | Converts to NMN, then NAD |
| Absorption | Specific Slc12a8 transporter | Passive diffusion/ENT transporters |
| Research Focus | Muscle, vascular health, endurance | Brain health, inflammation, liver |
| Best For | Physical performance & metabolism | Neuroprotection & general aging |
Conclusion: Is the Hype Justified?
The anti-aging hype surrounding NAD boosters is grounded in legitimate, groundbreaking biochemistry. While no supplement is a magic pill that stops time, the ability to support mitochondrial function and provide the fuel for sirtuins is a powerful tool in the modern longevity toolkit.
Whether you choose NMN or NR, the goal remains the same: maintaining the cellular energy of your youth to support a longer, healthier life. As with any supplement, it is vital to prioritize purity, third-party testing, and a foundation of good nutrition and exercise.