Learn ideal dosing timing and safety concerns.
Ashwagandha & Rhodiola: Your Adaptogenic Arsenal for Stress Resilience
In our increasingly demanding world, chronic stress has become an almost universal experience, silently chipping away at our physical and mental well-being. From affecting sleep and mood to impacting immune function, the sustained pressure of modern life can be detrimental. Fortunately, nature offers powerful allies to help the body navigate these challenges: adaptogenic herbs. These unique botanicals work non-specifically to increase the body's resistance to physical, chemical, and biological stressors, helping to restore balance, or homeostasis.
This comprehensive guide delves into the science of adaptogens, focusing on two of the most well-researched and potent options: Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) and Rhodiola (Rhodiola rosea). We will explore how these adaptogenic herbs function, their specific ashwagandha benefits, and how strategic dosing timing can maximize their impact on managing stress, reducing fatigue, and improving overall quality of life.
Understanding Adaptogens: The Science of Stress Tolerance
The term "adaptogen" was coined by N.V. Lazarev in 1947 and later defined by Israel Brekhman based on three core criteria:
-
Non-Specific Resistance: An adaptogen must help the body resist a broad spectrum of adverse conditions (stressors).
-
Normalizing Action: It must exert a normalizing influence on physiology, irrespective of the direction of the pathological state (e.g., it can help lower high cortisol but won't lower already normal cortisol too much).
-
Safety: It must be non-toxic and not cause major side effects.
The primary mechanism of action for adaptogens involves the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis and the Sympathoadrenal System (SAS), which are the body's central stress response pathways. When faced with a stressor, the HPA axis initiates a cascade of hormonal releases, culminating in the secretion of cortisol, the body's main stress hormone, from the adrenal glands.
Chronic, unmanaged stress leads to sustained HPA axis activation and excessive cortisol reduction. Over time, this constant state of alert can lead to adrenal fatigue, immune suppression, and a breakdown of metabolic function. Adaptogens, like Ashwagandha and Rhodiola, modulate this response. They essentially "tune down" the stress signaling system, particularly the excessive release of cortisol, allowing the body to maintain stability and enhance stress tolerance.
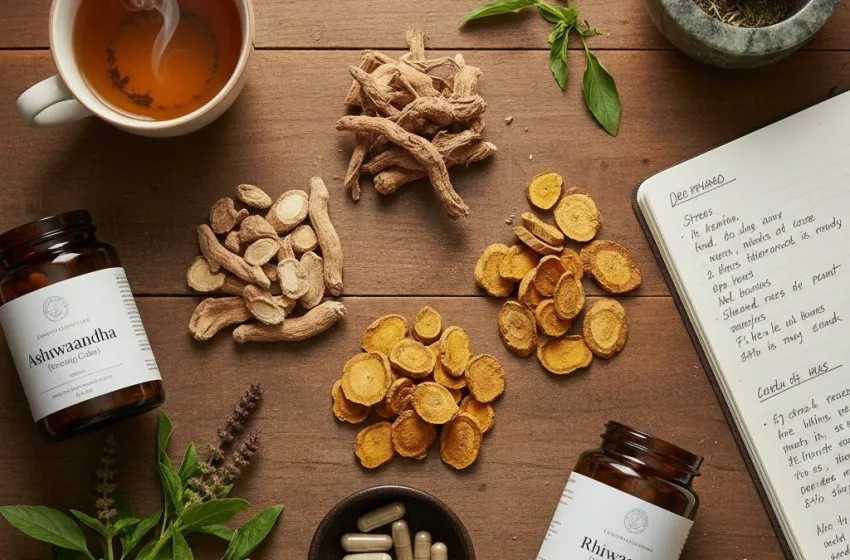
Ashwagandha: The Ayurvedic Calmer for HPA Axis Modulation
Ashwagandha, often called the "Indian Ginseng," has been a cornerstone of Ayurvedic medicine for thousands of years. Its name, literally meaning "smell of the horse," alludes to its traditional use for promoting vitality and strength.
Key Active Components and Mechanism
The primary active compounds in Ashwagandha are withanolides, a group of naturally occurring steroids. These compounds are believed to be responsible for the plant's therapeutic effects, particularly its profound anxiety-reducing and HPA axis-modulating properties.
Ashwagandha Benefits: Anxiety, Sleep, and Cortisol Control
Research on Ashwagandha points to several key advantages:
-
**Significant Cortisol Reduction: This is perhaps the most celebrated of all ashwagandha benefits. Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated Ashwagandha's ability to significantly lower serum cortisol levels in chronically stressed individuals. By buffering the impact of chronic stress on the HPA axis, it helps prevent the downstream negative effects of high cortisol, such as weight gain, immune suppression, and cognitive decline.
-
Anxiolytic (Anti-Anxiety) Effect: Ashwagandha interacts with the body's GABAergic system (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid), which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter. By promoting GABA activity, it helps calm the central nervous system, making it an excellent natural mood supplement for generalized anxiety and nervousness.
-
Improved Sleep Quality: Due to its calming effects, Ashwagandha has been shown to improve sleep onset and quality. The species name, somnifera, actually means "sleep-inducing," highlighting this traditional use.
-
Enhanced Strength and Recovery: Beyond stress, Ashwagandha is used to improve muscle mass and strength, particularly in conjunction with resistance training, and aids in post-exercise recovery.
Optimal Dosing Timing: Ashwagandha at Night
Given its relaxing and sedative qualities, the optimal dosing timing for Ashwagandha is typically in the evening or before bed.
Taking Ashwagandha at night aligns with its action as a primary "stress-reducer" and "calmer." It supports the natural nighttime dip in cortisol levels and promotes the deep, restorative sleep necessary for optimal physical and mental recovery from the day's stressors. A typical dosage ranges from 300 to 600 mg of a high-quality root extract (standardized to $\geq 5\%$ withanolides).
Rhodiola Rosea: The Energy Booster for Mental and Physical Performance
Rhodiola, also known as Golden Root or Arctic Root, has a long history of use in traditional medicine in Russia and Scandinavian countries to enhance physical endurance, mental acuity, and resistance to high-altitude sickness and cold environments.
Key Active Components and Mechanism
The primary active compounds in Rhodiola are rosavins and salidrosides. Unlike Ashwagandha, which tends to be more calming, Rhodiola is considered a stimulatory adaptogen.
Rhodiola is thought to work by influencing the levels of key monoamines, such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, in the brain. It helps preserve these neurotransmitters, which are often depleted during chronic stress, making it effective for combating fatigue. It also appears to protect mitochondria—the "powerhouses" of the cells—from stress-induced damage, thereby enhancing cellular energy production.
Rhodiola Benefits: Fatigue, Focus, and Energy
The documented benefits of Rhodiola focus heavily on cognitive and physical stamina:
-
Anti-Fatigue and Energy Enhancement: Rhodiola excels at improving both mental and physical capacity, especially in high-stress, low-performance situations. It is highly effective for reducing symptoms of burnout and general fatigue.
-
Improved Cognitive Function and Focus: By optimizing neurotransmitter activity, Rhodiola helps enhance concentration, working memory, and the ability to perform complex mental tasks under pressure.
-
**Enhanced Stress Tolerance: While it doesn't dramatically lower cortisol like Ashwagandha, Rhodiola improves the cell's response to stress by making it more efficient and resilient, thus increasing the total capacity for work. It works to improve the body's stress tolerance without causing overstimulation.
-
Mood Improvement: As a natural mood supplement, Rhodiola can help alleviate mild depressive symptoms, likely due to its influence on serotonin and dopamine pathways.
Optimal Dosing Timing: Rhodiola in the Morning
Because of its mildly stimulating and performance-enhancing effects, the ideal dosing timing for Rhodiola is in the morning or early afternoon.
Taking Rhodiola in the morning helps set the stage for a day of enhanced focus, improved energy levels, and increased physical and mental stress tolerance. Taking it later in the day may interfere with sleep due to its energizing nature. A typical dosage of a high-quality extract (standardized to $\geq 3\%$ rosavins and $\geq 1\%$ salidrosides) is between 200 and 400 mg.
Synergy: Combining Ashwagandha and Rhodiola
Many individuals find the greatest benefit in combining these two powerful adaptogenic herbs to cover the full spectrum of stress management:
| Adaptogen | Primary Effect | Best Dosing Timing | Use Case |
| Ashwagandha | Calming, Anxiolytic, Cortisol Reduction | Evening/Bedtime | Chronic stress, anxiety, sleep issues, HPA axis hyperactivity. |
| Rhodiola | Stimulating, Anti-fatigue, Cognitive Enhancer | Morning/Early Afternoon | Acute stress, mental fog, physical fatigue, demanding work periods. |
By using Rhodiola in the morning, you benefit from enhanced energy and focus to tackle the day's stressors, while using Ashwagandha at night supports nervous system repair and ensures deep, restorative sleep. This stacked approach provides a 24-hour cycle of stress resilience.
Important Considerations: Safety Concerns and Usage
While generally well-tolerated, it is crucial to address safety concerns and proper usage when incorporating adaptogenic herbs into your routine.
General Safety and Contraindications
-
Consult a Professional: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking prescription medications.
-
Autoimmune Conditions: Ashwagandha may potentially stimulate the immune system, so individuals with autoimmune diseases (e.g., Hashimoto's, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus) should use it with caution and medical supervision.
-
Thyroid Function: Ashwagandha can increase thyroid hormone levels. Individuals on thyroid medication must monitor their TSH levels closely.
-
Bipolar Disorder: Rhodiola's stimulating effects could potentially trigger mania in susceptible individuals with Bipolar Disorder.
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Neither herb is recommended for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to a lack of sufficient safety data.
Quality and Standardization
The efficacy of adaptogenic herbs is highly dependent on the quality and standardization of the supplement. Always look for extracts standardized to their active compounds (withanolides for Ashwagandha; rosavins and salidrosides for Rhodiola) to ensure you are getting a therapeutic dose.
Dosing Timing and Cycling
Adhering to the recommended dosing timing (Rhodiola morning, Ashwagandha night) is key. Additionally, some practitioners recommend cycling adaptogens—taking them for a period (e.g., 6-12 weeks) and then taking a short break—to prevent the body from becoming overly accustomed to their effects and to ensure sustained efficacy.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Modern Stress
Chronic stress is an inevitable part of the modern human experience, but it doesn't have to define your health. By understanding and strategically utilizing the power of adaptogenic herbs like Ashwagandha and Rhodiola, you gain two distinct tools for building exceptional stress tolerance. Ashwagandha offers calm, significant cortisol reduction, and deeper sleep when taken at night, while Rhodiola provides focused energy and enhanced performance when taken in the morning. By making these powerful botanicals a part of your daily routine, you move from merely coping with stress to cultivating genuine physical and mental resilience, supported by the time-tested wisdom of nature and modern science.