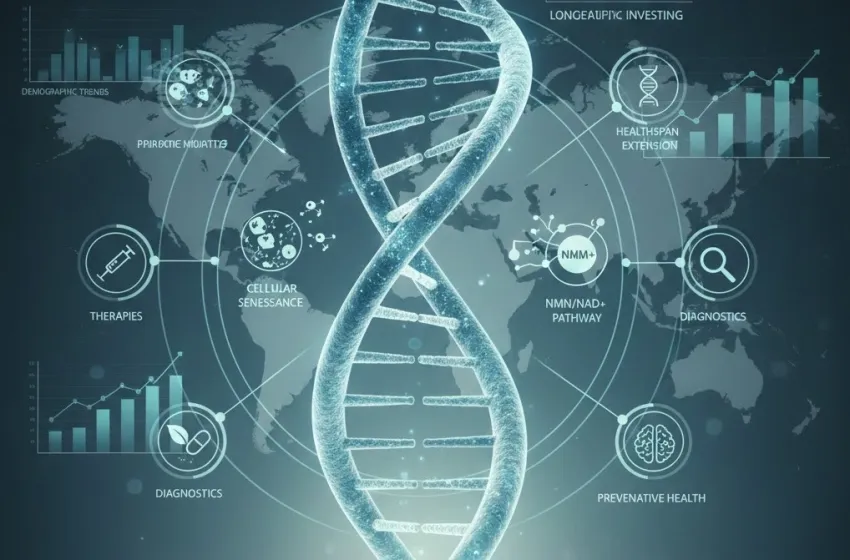
Explore the trillion-dollar opportunity in longevity investing & healthspan tech.
The concept of extending life is no longer confined to the realm of science fiction. We are at the cusp of a profound societal and biological transformation, driven by breakthroughs in molecular biology, genetics, and artificial intelligence. This shift has unlocked a colossal new market for longevity investing, moving the focus from merely extending lifespan (the total years lived) to dramatically extending healthspan (the years lived in good health).
The fundamental economic and human case for investing in this sector is compelling. Chronic, age-related diseases account for a vast majority of the global disease burden and healthcare costs. By targeting the root mechanisms of aging, healthspan tech aims to compress the period of morbidity, allowing people to remain functional, productive, and independent for longer. This not only offers immense human value but promises to unlock trillions of dollars in economic value by boosting workforce productivity and reducing the crushing burden of age-related healthcare expenditure.
Understanding the Biological Imperative: The Science of Aging
The foundation of anti-aging biotech is geroscience—the study of aging as a malleable biological process, not an inevitable fate. Researchers have identified several "hallmarks of aging" that represent the core cellular and molecular damage accumulated over time. Investment is now flowing into companies developing therapies and diagnostics that directly target these hallmarks.
Targeting Cellular Senescence
One of the most promising areas is addressing cellular senescence. Senescent cells are damaged cells that stop dividing but refuse to die, instead secreting pro-inflammatory molecules that disrupt tissue function and drive age-related diseases like arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegeneration. They are, essentially, "zombie cells" that harm their neighbors.
Investment Opportunity: Companies are focused on developing senolytics—drugs designed to selectively clear these senescent cells from the body. Early clinical trials show promising results in reducing age-related dysfunction, opening up a potential market that spans dozens of common chronic diseases.
The NAD Pathway and Metabolic Health
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD ) is a vital coenzyme found in all living cells, essential for metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression. Crucially, cellular levels of NMN/NAD decline dramatically with age, correlating directly with a decrease in cellular function and energy production.
Investment Opportunity: Companies are developing and testing NAD precursors like Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), as well as novel delivery systems and formulations. The goal is to safely and effectively restore youthful NAD levels to bolster mitochondrial function and cellular resilience, with potential applications ranging from cognitive health to muscle strength.
Investment in Therapies, Diagnostics, and Tools
Investment in companies developing therapies, diagnostics, and tools focused on extending the period of human health and reducing chronic disease is accelerating across the entire value chain. This goes far beyond just drug discovery, encompassing four core segments:
1. Therapeutics and Drug Discovery
This segment includes the core anti-aging biotech firms working on novel pharmacological interventions.
Targeting the Hallmarks: This includes the aforementioned senolytics, as well as senomorphics (drugs that stop senescent cells from secreting inflammatory signals), and gene-editing technologies like CRISPR being explored for age-related gene repair.
Reprogramming: Advanced therapies like partial cellular reprogramming aim to "reset" the biological age of cells, turning back the epigenetic clock to restore tissue function, an area attracting billions in funding from major investors.
The Big Picture: The ultimate prize here is a single drug that addresses aging as a master process, thereby preventing multiple diseases simultaneously—a paradigm shift for the pharmaceutical industry.
2. Diagnostics and Biomarkers
You can't manage what you don't measure. The field requires new tools to accurately measure biological age versus chronological age, establishing endpoints for clinical trials, and monitoring patient progress.
Epigenetic Clocks: Companies are developing sophisticated blood and saliva tests that measure methylation patterns on DNA to provide an accurate reading of a person's biological age.
Multi-Omics Platforms: Investments in platforms that integrate genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data with AI are crucial for identifying new targets, stratifying patient risk, and personalizing preventative health strategies.
Digital Biomarkers: Wearables and continuous monitoring devices (part of the broader AgeTech space) are generating longitudinal data on sleep, activity, heart rate variability, and other factors that act as real-time healthspan diagnostics.
3. Preventative Health and Consumer Wellness
While biotech focuses on radical intervention, the more immediate investment opportunities exist in empowering individuals to manage their healthspan proactively.
Nutraceuticals and Supplements: The market for science-backed compounds like NMN, Metformin, and Rapamycin analogs continues to grow, attracting capital into formulation, delivery, and clinical validation.
Precision Nutrition/Wellness: Companies leveraging AI to offer personalized dietary, exercise, and lifestyle recommendations based on an individual's unique genetics and biomarkers are gaining traction. This is a crucial area for early intervention and is closely tied to preventative health.
4. Healthcare Infrastructure and Delivery
The infrastructure to deliver these new longevity solutions needs to be built.
Longevity Clinics: A growing network of specialized clinics offers advanced diagnostics, personalized intervention plans, and health coaching. Investment here supports scale and standardization.
AI for R&D: Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning are becoming indispensable tools for accelerating drug discovery, identifying drug repurposing candidates, and managing the vast datasets generated by longevity research.
The Macroeconomic Tailwind: Demographic Trends
The investment case is powerfully supported by irrefutable demographic trends. The global population is aging at an unprecedented rate.
- By 2050, the number of people aged 65 and over is projected to double, reaching 1.6 billion.
This inversion of the age pyramid presents immense challenges to pension systems, labor markets, and healthcare infrastructure, unless those extra years are spent in good health.
Longevity investing is the market's response to this megatrend. Extending healthspan transforms a looming economic crisis into an economic opportunity. Healthier, older adults can remain active in the workforce, continue to contribute to their communities, and avoid costly long-term care and hospital stays associated with chronic disease. The World Bank and McKinsey Health Institute have quantified the immense economic returns, suggesting that even a modest increase in healthy life expectancy is worth trillions of dollars globally.
Conclusion: A New Era of Health and Wealth
The transition from "sickcare" to "healthcare" is defining the next century of medical and technological innovation. Longevity investing in healthspan tech is not a speculative bet on immortality; it is a pragmatic, economically rational strategy focused on addressing the single largest risk factor for global health expenditure: biological aging itself. Companies targeting core mechanisms like cellular senescence and metabolic pathways, leveraging compounds like NMN/NAD , and building the necessary diagnostics and tools are at the vanguard of this revolution.
Against the backdrop of unavoidable demographic trends, this sector offers the rare combination of massive human benefit and extraordinary financial upside. For investors, the question is no longer if healthy longevity will transform society, but which companies will lead the way in extending the period of human health and reducing chronic disease.