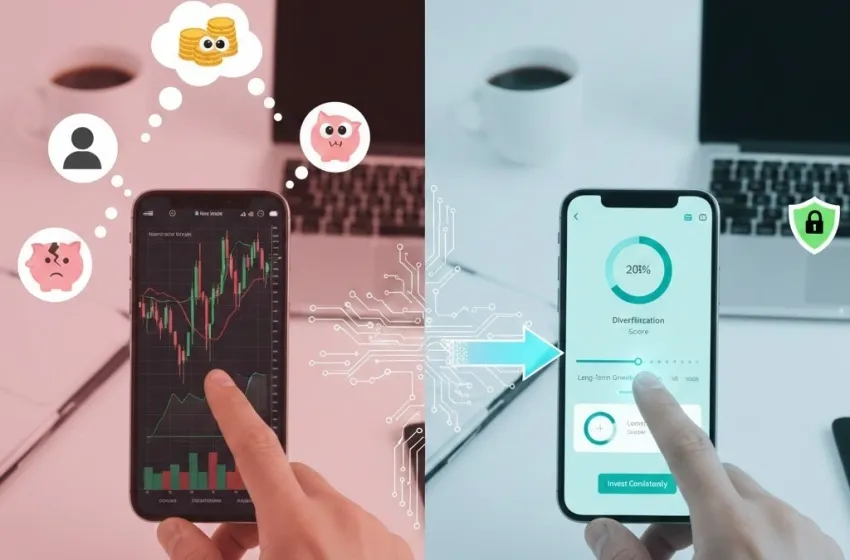
Discover how Behavioral finance applies to FinTech.
The world of investing is often portrayed as a purely rational domain, driven by hard data and logical analysis. Yet, the reality is that markets are shaped by human beings, whose financial decision-making is heavily influenced by emotion and ingrained mental shortcuts. Behavioral finance is the field that recognizes this gap, merging the principles of psychology and economics to explain why investors frequently act against their own best interest. Understanding the mechanisms of investor psychology is the first step toward building better financial tools.
The Tyranny of Cognitive Biases
At the core of irrational investing are cognitive biases—systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. These biases manifest in destructive ways, leading to common errors like selling low or chasing bubbles. For instance, loss aversion—the psychological phenomenon where the pain of a loss is roughly twice as powerful as the pleasure of an equivalent gain—is one of the most detrimental biases. It causes investors to hold onto declining assets too long, hoping to break even, or to sell profitable assets prematurely to "lock in" the gain, thereby limiting long-term returns.
Other common biases include:
- Confirmation Bias: Seeking out information that confirms existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence.
- Herding: Following the crowd, often leading to market bubbles or panic selling.
- Anchoring: Over-relying on the initial piece of information (the "anchor") when making subsequent decisions.
Applying Psychological Principles to FinTech Design
Modern FinTech platforms are uniquely positioned to tackle these psychological pitfalls through the strategic implementation of investment nudges. These are subtle, non-coercive prompts or changes in the user interface (UI) design that guide the user toward a more rational choice without restricting their freedom. This approach shifts the burden from the investor's limited willpower to the platform's design architecture.
How Automated Nudges Work in Practice
The design goal is to create a "frictionless" path to good habits and a "sticky" path for bad ones.
| Bias Addressed | FinTech Nudge/Design Element | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Loss aversion | Default Enrollment in Diversification: Automatically allocate new funds across a pre-set diversified portfolio unless the user explicitly opts out. | Leverages the status quo bias to ensure diversification, reducing the chance of single-stock panic sales. |
| Herding | Long-Term Performance Context: When a user is viewing a highly volatile stock, the platform displays its 10-year return alongside the 1-month return. | Provides perspective to counter the impulse to follow short-term trends, promoting a long-term view. |
| Present Bias | Commitment Contracts: A feature that allows a user to "lock" a portion of their investment, requiring a 7-day waiting period to withdraw it. | Creates friction for impulsive withdrawals, reinforcing the user's initial commitment to save. |
| Anchoring | Framing of Savings Goals: Frame saving not in terms of total dollar amount, but as a percentage of salary needed to sustain a desired future lifestyle. | Shifts the anchor away from arbitrary numbers toward the meaningful consequence of their actions. |
The Future of Financial Decision-Making
The synergy between Behavioral finance and FinTech design is transforming how people engage with their money. By employing automated nudges, FinTech companies move beyond merely providing data to actively improving user outcomes. This paradigm shift, centered on understanding investor psychology and mitigating the impact of cognitive biases, is crucial for democratizing effective investing and helping individuals achieve better long-term wealth accumulation by overcoming primal instincts like loss aversion. This approach ensures that technology acts as a safeguard against human irrationality, guiding users away from destructive habits like selling low or chasing bubbles toward consistent, disciplined growth.