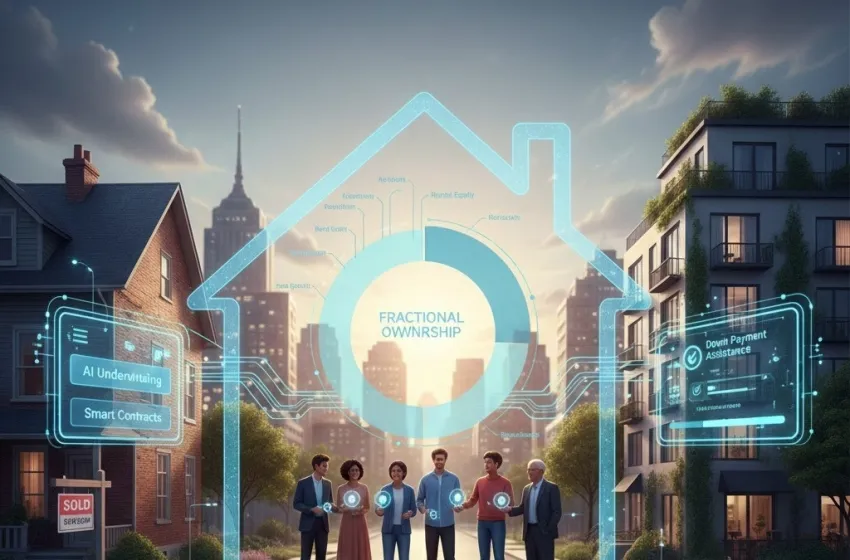
Learn how FinTech mortgage innovations lower costs and expand homeownership.
The global housing crisis solutions often seem insurmountable, characterized by soaring property values, stagnant wages, and a crippling barrier to entry for first-time buyers and low-to-moderate-income families. The traditional mortgage and real estate industries, built on slow, paper-heavy processes and rigid credit models, have struggled to adapt to this crisis, inadvertently widening the gap between aspiration and ownership.
Enter FinTech mortgage, a transformative force leveraging technology to dismantle historic inefficiencies, lower costs, and crucially, democratize access to homeownership and real estate investment. Technology companies are not just making the existing process faster; they’re creating new models for Affordable housing finance and expanding the very definition of who is mortgage-eligible.
The FinTech Revolution in Mortgage Lending
The mortgage process has historically been a lengthy, opaque, and expensive ordeal. Every step, from application to underwriting to closing, was an administrative bottleneck that contributed to high origination costs—costs ultimately borne by the borrower. FinTech is tackling this head-on with digital lending innovations that streamline the entire lifecycle.
Streamlining and Lowering the Cost of Mortgages
Technology companies are creating products to streamline and lower the cost of mortgages and make housing investment more accessible by applying the principles of automation, AI, and big data.
Automated Underwriting and AI: Traditional underwriting is labor-intensive and relies on a narrow set of criteria, primarily the FICO score. FinTech platforms use Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to instantly process vast amounts of data—including non-traditional data points like rent payments, utility bills, and cash flow analysis from bank statements. This not only accelerates loan approvals from weeks to days (or even minutes) but also reduces the human capital required, directly lowering a lender’s operational costs. These savings can then be passed on to the borrower in the form of lower fees and more competitive rates.
The Paperless Mortgage: Through Robotic Process Automation (RPA), digital-first lenders eliminate physical paperwork. Tools like e-signatures, automated document recognition, and direct API (Application Programming Interface) connections to banks and employers allow borrowers to complete applications and verify information entirely online. This simplifies the process, cuts down on errors, and further reduces the "time-to-close," making the entire experience far more efficient.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts: Blockchain technology introduces a tamper-proof, decentralized ledger for recording property ownership, title transfers, and mortgage payments. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded to automatically release funds and transfer ownership once predefined conditions (like final loan approval) are met. This has the potential to drastically reduce the need for intermediaries like title companies and escrow agents, which are significant sources of closing costs.
Enhancing Accessibility with Alternative Credit Scoring
The biggest barrier for many low-to-moderate-income and younger buyers is not necessarily an inability to pay, but a lack of sufficient traditional credit history. FinTech solutions are pioneering the use of alternative data for creditworthiness assessment.
Rental History and Utility Payments: Companies are creating models that analyze consistent, on-time rent and utility payments, which are strong indicators of financial responsibility but are often ignored by traditional credit bureaus. This holistic view of a borrower’s financial life allows lenders to serve the "credit-invisible" or those with thin files, expanding the pool of qualified buyers for affordable housing finance.
Personalized Loan Products: Advanced analytics allow FinTechs to model risk more precisely, moving away from a one-size-fits-all loan offering. This leads to personalized loan terms and repayment options tailored to an individual’s specific income stream and financial profile, which is particularly beneficial for contract workers or those with non-traditional employment.
Innovative Solutions for Down Payment and Investment
Even with streamlined mortgages, the single largest hurdle remains the down payment assistance. FinTech is addressing this by creating innovative savings and investment vehicles that reduce the upfront capital required to access the housing market.
Disrupting the Down Payment Barrier
The average down payment for a first-time homebuyer is a significant financial challenge. FinTech is providing new avenues for saving and accessing funds.
Down Payment Assistance (DPA) Aggregators: Platforms are emerging that act as central hubs for aggregating and matching borrowers with the thousands of federal, state, and local DPA programs. By automating the search and application process for these complex programs, they ensure eligible buyers don't miss out on crucial funding.
Rent-to-Own and Equity-Sharing Models: Some companies operate under a rent-to-own model where they buy the home a family chooses and leases it back to them for a set period. A portion of the rent is often set aside as an equity credit, which the tenant can then use toward purchasing the home at a predetermined price at the end of the lease. This allows families to secure their home's price while they save for the full down payment, insulating them from rapid appreciation and helping them avoid the rental-trap cycle.
The Rise of Fractional Real Estate
Beyond homeownership, FinTech is making real estate investment itself more accessible, tackling the supply-side issue and diversifying wealth creation.
Fractional real estate platforms leverage tokenization (often using blockchain) or simply modern legal structures to allow individuals to buy a "fraction" or share of a high-value property—residential or commercial—for a minimal initial investment.
Democratizing Investment: This model lowers the entry point for real estate investing from tens of thousands of dollars to as little as a few hundred. By enabling more investors to participate, it frees up capital, provides liquidity, and allows individuals to diversify their portfolios without the burden of full property management. While often focused on investment properties like vacation homes or rentals, the underlying technology points to a future where shared equity or smaller, securitized portions of residential properties could become an option for first-time buyers.
FinTech as a Solution to the Housing Crisis
The true potential of FinTech lies in its ability to contribute meaningful housing crisis solutions by improving efficiency and expanding financial inclusion.
| Traditional Lending | FinTech Digital Lending | Impact on Affordability |
|---|---|---|
| Manual document processing, high overhead. | Automated RPA & AI processing, low operational cost. | Lower origination fees and closing costs. |
| Reliance on FICO Score and credit history. | Uses Alternative Data (rent, utility, cash flow). | Expands eligibility to credit-invisible/thin-file buyers. |
| Fragmented process (appraiser, underwriter, title). | Integrated API ecosystem with automated tracking. | Faster closing times, reduces opportunity cost. |
| High cost/capital barrier to real estate investment. | Fractional real estate platforms with low entry points. | Democratizes wealth creation and investment in housing supply. |
The impact of digital lending goes far beyond customer convenience. By drastically reducing the administrative friction and cost of originating a mortgage, FinTech allows more capital to flow into the housing market, potentially incentivizing development or rehabilitation of affordable housing units. Furthermore, the ability to accurately assess risk on non-traditional borrowers makes a wider range of loan products viable, ultimately supporting Affordable housing finance initiatives that traditional institutions deemed too risky or costly to service.
The integration of RegTech (Regulatory Technology) within FinTech platforms also ensures that speed and innovation don't compromise security or compliance. Automated compliance checks help lenders adhere to fair lending practices and prevent discrimination, making the expanded access both responsible and equitable.