Explore Autonomous Database and Self-Healing Systems,
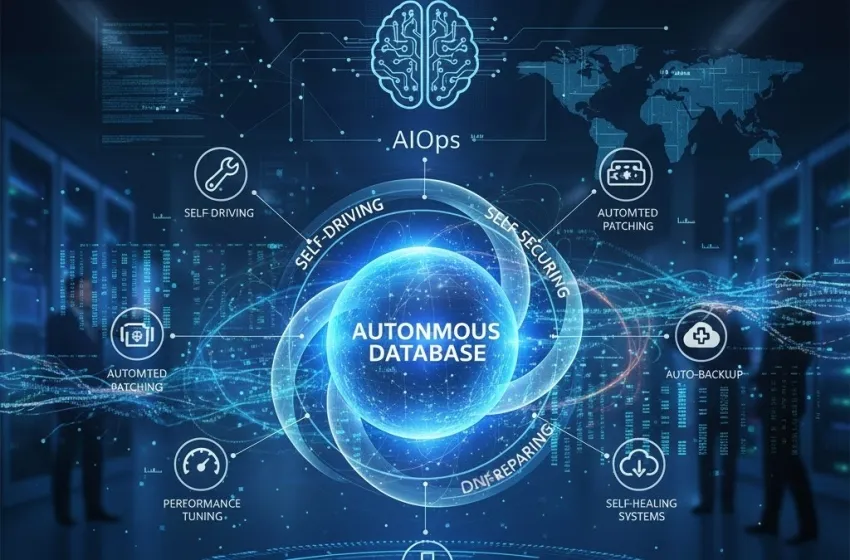
The complexity of modern enterprise IT infrastructure, coupled with the relentless demand for 24/7 availability, has pushed traditional database administration models to their breaking point. Managing mission-critical data stores—which require continuous monitoring, tuning, patching, and backup—has become a massive drain on time and resources. Enter the revolutionary concept of the **Autonomous database** and **self-healing systems**, a paradigm shift that promises to eliminate manual overhead, drastically reduce downtime, and liberate IT staff to focus on innovation.
This new class of database management is fundamentally reshaping the relationship between humans and data infrastructure. By leveraging the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), these systems are designed to **automatically patch, tune, backup, and repair themselves without human intervention**, leading to unprecedented levels of efficiency, security, and resilience.
Autonomous Database: The Core of Intelligent Operations
An **Autonomous database** is a fully managed cloud database service that uses machine learning to automate the entire lifecycle of database operations. Unlike conventional databases, which are often co-managed and require significant hands-on administration, an autonomous database is *self-driving*, *self-securing*, and *self-repairing*.
This self-management capability extends to every aspect of routine database administration, essentially eliminating human error and manual labor for mundane yet critical tasks. The core promise is simple: IT professionals can load their data and focus purely on leveraging it for business value, while the database itself handles the operational heavy lifting.
Key Automated Functions
The automation within an autonomous database encompasses several critical areas:
- Auto-Provisioning and Configuration: Databases are deployed and optimized for specific workloads (transaction processing, data warehousing, etc.) automatically. Configuration parameters, memory, and access structures are continually tuned by the system.
- Auto-Scaling: The system automatically scales compute and storage resources up or down based on real-time workload demand. This ensures that the database always has the resources it needs during peak times while optimizing costs during lulls—a true pay-per-use model. All scaling occurs online without interrupting application services.
- Auto-Indexing: The database constantly monitors SQL workloads and uses machine learning to detect missing indexes that could improve query performance. It validates the potential benefit of a new index before implementing it, and critically, it learns from its own decisions to improve future recommendations.
- Automated Backups and Recovery: The system performs automatic daily backups, offering point-in-time recovery capabilities and ensuring data durability with no manual scheduling or management required.
The synergy of these automated features results in a database that is always on, always optimized, and always secure.
Self-Healing Systems: Beyond Automation
While automation handles routine tasks, **self-healing systems** represent the next evolution, focusing on resilience and recovery. A self-healing system is an automated framework designed to detect, diagnose, and rectify faults and disruptions autonomously, maintaining optimal functionality without human intervention. This capability is what guarantees the promised high-availability and reliability.
A self-healing database operates on a principle of **proactive and reactive recovery**:
- Autonomous Detection and Diagnosis: Continuous, real-time monitoring of the database and its underlying infrastructure (hardware, network, operating system) is performed. Machine learning models analyze logs, metrics, and events to identify subtle anomalies, forecast performance bottlenecks, and predict potential hardware or software failures *before* they occur. This goes beyond simple alerting—it's about anticipating failure.
- Automated Recovery and Rectification: Once an issue is detected, the system immediately launches corrective actions.
- Fault Isolation: If a component fails (e.g., a server node), I/O operations are instantly redirected around the unhealthy device to maintain service continuity.
- Failover Mechanisms: For critical failures, the system automatically fails over to a redundant, synchronized standby database (often utilizing technologies like Autonomous Data Guard) with **zero-data loss** to ensure transparent application continuity for end-users.
- Software Repair: The system can automatically apply known fixes, restart faulty processes, or reconfigure parameters to restore optimal performance.
This self-repairing nature significantly reduces Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR), which is a key metric in modern IT operations. By handling the vast majority of incidents autonomously, human intervention is only required for the most complex or novel issues.
The Role of AIOps in Self-Healing
The entire ecosystem of autonomous and self-healing IT is underpinned by **AIOps** (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations). AIOps platforms use machine learning to ingest and analyze massive volumes of operational data (logs, metrics, and events) from across the entire IT estate.
**AIOps** acts as the brain of the **self-healing systems**, providing the necessary intelligence to achieve true autonomy:
- Anomaly Detection: ML algorithms are trained on historical data to understand "normal" system behavior. Any statistically significant deviation—an anomaly—triggers an alert or, more often, an automated remediation action.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): AIOps correlates events across different layers (application, database, infrastructure) to accurately pinpoint the true root cause of an issue, eliminating the need for manual, time-consuming log sifting.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using models like time-series analysis and regression, AIOps can forecast when a component might fail or when performance is likely to degrade, triggering preventative actions like scaling up resources or initiating **automated patching** *before* an issue impacts the business.
- Closed-Loop Automation: AIOps enables a fully automated cycle of detection, diagnosis, decision, and execution. The system learns from every resolution, continuously refining its knowledge base and making future responses faster and more accurate.
Automated Patching and Zero-Downtime Maintenance
Security and compliance mandates require systems to be consistently patched and updated, but manual patching is a notorious source of downtime and human error. The **Autonomous database** addresses this with **automated patching** as a core feature.
- Continuous Security: Security vulnerabilities and bugs are automatically identified, and the necessary patches are applied by the system itself. This ensures the database is perpetually up-to-date against both external attacks and malicious internal users, mitigating concerns about unpatched systems.
- Zero-Downtime Maintenance: The process of patching and upgrading occurs in a rolling fashion across a cluster of nodes or servers. Utilizing techniques like application continuity and intelligent connection rerouting, user sessions and applications remain running without interruption. This commitment to **zero-downtime maintenance** means that scheduled and unplanned maintenance events become invisible to end-users and business applications, guaranteeing a higher SLA (Service Level Agreement) and vastly improved user experience.
Performance Tuning: The Perpetual Optimizer
Traditional database administrators spend a significant portion of their time on **performance tuning**—analyzing query plans, optimizing SQL code, managing memory allocation, and modifying initialization parameters. In an **Autonomous database**, this is entirely automated.
The database constantly monitors the workload and employs machine learning to:
- Dynamic Query Optimization: The optimizer automatically adapts execution plans and resource allocation for different query patterns in real-time.
- Memory Management: The system dynamically adjusts memory structures (e.g., buffer caches, shared pools) based on actual workload usage, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
- Configuration Self-Tuning: The database identifies and adjusts thousands of configuration parameters to optimize for the specific workload (e.g., OLTP, Data Warehouse, Mixed), often achieving performance gains that a human DBA might struggle to match.
Conclusion: A Future Without Database Administration
The evolution from traditional databases to the **Autonomous database** represents the future of enterprise data management. These systems, powered by **AIOps** and built with **self-healing systems** principles, are fundamentally changing the role of IT professionals. By automatically handling routine tasks like **automated patching**, backups, and **performance tuning**, and guaranteeing **zero-downtime maintenance**, they transform DBAs from reactive 'firefighters' into strategic architects focused on data innovation and higher-value business projects. In this new era, the database manages itself, ensuring maximum availability, security, and performance, allowing businesses to thrive at the speed of the cloud.