Maximize Your Healthspan with NAD & Senolytics
The aging process is no longer viewed as an unchangeable fate but rather as a biological process driven by a set of interconnected mechanisms, often referred to as the "Hallmarks of Aging." Targeting these hallmarks is the core strategy for extending healthspan.
The Threat of Cellular Senescence
One of the most critical hallmarks and a major target of research is cellular senescence.
What it is: Senescence is a state where cells stop dividing but do not die. This irreversible cell cycle arrest occurs in response to stress, damage, or as cells reach their division limit.
The Problem: While senescent cells play protective roles (like preventing cancer by halting damaged cell division), their accumulation with age is detrimental. They release a toxic mix of pro-inflammatory molecules, growth factors, and proteases known as the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP).
The Impact: The SASP induces chronic, low-grade inflammation throughout the body—often called "inflammaging"—and damages surrounding healthy tissue, driving age-related diseases like cardiovascular disease, neurodegeneration, and metabolic dysfunction.
Targeted Interventions: Senolytics are a class of anti-aging compounds being developed to selectively kill senescent cells, while senomorphics aim to suppress the harmful SASP without killing the cells. Natural compounds like fisetin and quercetin are prominent examples being studied for their senolytic activity.
NAD Decline and Energy Metabolism
Another pivotal biological mechanism in longevity science is the role of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD ).
What it is: NAD is a vital coenzyme found in every cell. It is indispensable for over 500 enzymatic reactions, most notably in energy production (ATP) within the mitochondria (the cell's powerhouses) and as a crucial co-substrate for enzymes that regulate DNA repair and cellular health, such as sirtuins (SIRTs) and Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerases (PARPs).
The Problem: Cellular NAD levels decline dramatically with age, estimated to drop by up to 50% between young and old adulthood. This reduction cripples the cell's ability to produce energy, repair DNA damage, and activate the protective sirtuin pathways, effectively linking NAD decline to multiple hallmarks of aging.
Targeted Interventions: The market has seen an explosion of NAD boosters, which are precursor molecules designed to raise intracellular NAD levels. The most studied examples include Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN). Preclinical and initial human studies suggest that boosting NAD may improve mitochondrial function, muscle performance, and vascular health, directly supporting healthspan extension.
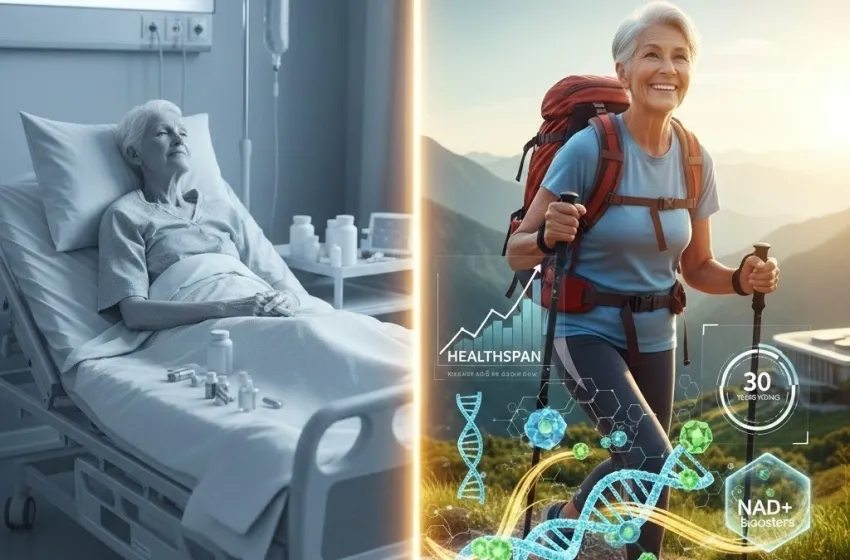
Healthspan vs. Lifespan: The Shift in Perspective
The core philosophical change in the modern longevity movement is the emphasis on healthspan vs. lifespan.
| Feature | Lifespan | Healthspan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The total duration of life, from birth to death. | The period of life spent in good health, free from major chronic disease and disability. |
| Traditional Goal | Quantity of years lived. | Quality of years lived. |
| Focus | Treating disease after it appears (reactive medicine). | Preventative medicine and proactively optimizing biological function (proactive). |
| Metric | Chronological age. | Biological age (how old your cells/systems function), often tracked by biomarkers. |
The traditional model of aging involves a relatively short, sharp decline into disease and frailty right before death. The goal of healthspan extension is the compression of morbidity—to significantly delay the onset of chronic, debilitating diseases, allowing a person to live a long, active, and independent life right up until the very end. This shift is not just medical; it is social and economic, promising a future with fewer years spent in dependency.
The Role of Anti-Aging Compounds and Preventative Medicine
The quest for a longer, healthier life is no longer confined to the lab. A massive consumer trend is aligning with cutting-edge longevity science, driving demand for evidence-based interventions under the umbrella of preventative medicine.
Anti-Aging Compounds (Nutraceuticals and Pharmaceuticals)
In addition to NAD boosters and senolytics, researchers are exploring other promising anti-aging compounds:
- Metformin: An existing diabetes drug that has shown pleiotropic effects in preclinical models, potentially by mimicking calorie restriction and modulating cellular energy pathways. It is currently the subject of the TAME (Targeting Aging with Metformin) clinical trial.
- Rapamycin: A powerful immunosuppressant used in transplant medicine, which inhibits the mTOR (mammalian Target of Rapamycin) pathway—a central regulator of cell growth, metabolism, and aging. In model organisms, it is one of the most effective compounds for extending both lifespan and healthspan.
- Resveratrol: A polyphenol found in red wine and grapes, which is a known activator of the Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) enzyme, linking its effects back to the NAD pathway and promoting cellular resilience.
- Taurine and GlyNAC: Amino acids and amino acid precursors, respectively, that have been shown to combat chronic inflammation, improve mitochondrial function, and, in some animal studies, dramatically extend lifespan and healthspan.
Preventative Medicine and Lifestyle
While molecular interventions capture headlines, the foundation of extended healthspan remains rooted in lifestyle choices—the truest form of preventative medicine:
- Nutrition: A focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods, often drawing from blue zones (areas of the world with the highest concentration of centenarians). This includes practices like intermittent fasting and the pursuit of functional foods rich in polyphenols and antioxidants.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, especially resistance training, is recognized as one of the most powerful "longevity drugs," mitigating sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss) and improving metabolic and cardiovascular health.
- Sleep and Stress Management: Optimization of sleep quality and effective stress management are now recognized as essential for maintaining DNA repair processes, hormonal balance, and overall cellular homeostasis, which are foundational to longevity.
- Biomarker Tracking: Consumers are increasingly adopting personalized health protocols, using blood work, genetic testing, and wearable technology (like Oura or continuous glucose monitors) to track their biological age and key longevity biomarkers. This allows for personalized, data-driven adjustments to their preventative strategies.